Introduction
Babylon is a new Cosmos project whose vision is to leverage the security of Bitcoin for enhancing the security of Cosmos zones and other PoS chains. In this first post, we will give a bird’s eye view of the project and in the subsequent posts, we will delve deeper into its the various use cases.
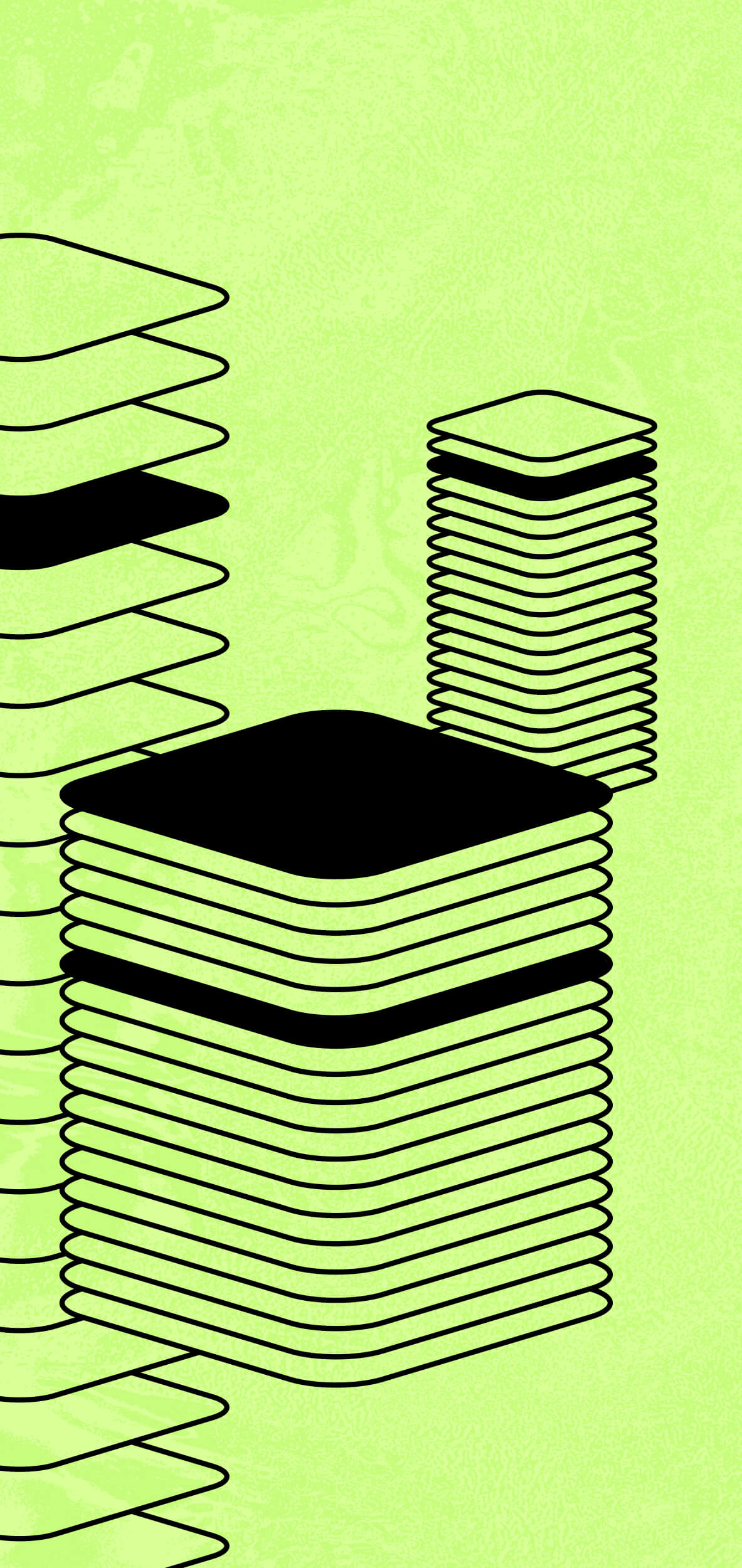
The Babylon architecture
The Babylon architecture is shown above. It consists of three components with two levels of checkpointing:
- Bitcoin, as the timestamping service.
- The Babylon chain, a Cosmos zone, as the middle layer.
- Other Cosmos zones, as the consumers of security.
An important design consideration is that Bitcoin has very limited capacity in carrying arbitrary data. In this context, the Babylon chain serves several functions:
- It aggregates the checkpoint streams of many consumer zones so that only one checkpoint stream needs to be inserted into Bitcoin to simultaneously timestamp events in all the consumer zones.
- Its checkpoints into Bitcoin can be made compact using cryptographic techniques such as aggregate signatures.
- It receives checkpoints from the consumer zones via Inter Blockchain Communication (IBC).
- It checks for the availability of the data behind the checkpoints of the consumer zones so that an attacker cannot timestamp unavailable data.
Technology
The Babylon technology which supports these use cases consists of 1) core primitives for writing timestamps onto Bitcoin by the consumer zones and reading the timestamps on Bitcoin by the consumer zones; 2) protocols that use the timestamp information to realize the various use cases. Both the core primitives and the protocols will be described in the following posts.
This article is also available on Substack: Babylon: Bitcoin Security for All (substack.com)